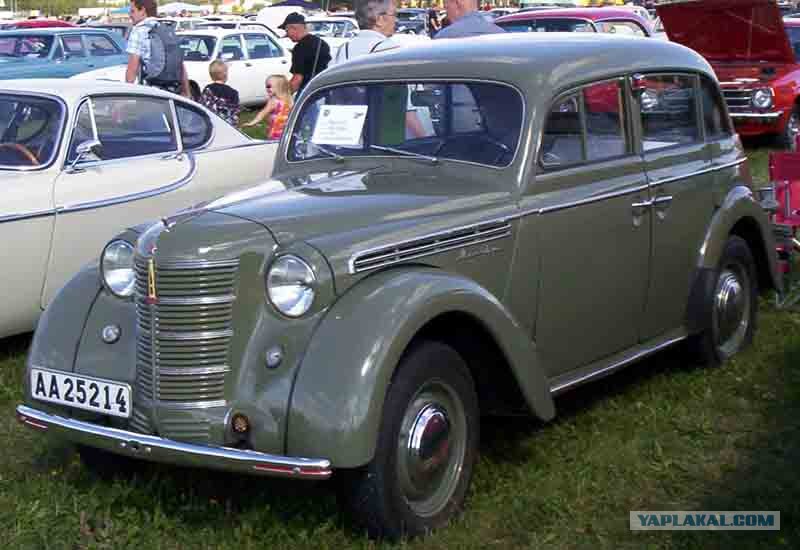
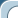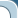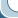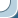Moskvich-400
Moskvich-400 - Soviet passenger car of small Germany, produced at the Plant of small cars in Moscow (ZMA, later - МЗМА) from December 1946 to 1954.
Originally was a full analogue of a car Opel cadet K38, produced in 1937-1940 years in Germany at the German branch Opel American concern General Motors, restored after the war, on the basis taken for the reparation of the copies of the documentation and tooling.
Moskvich-401 - an enhanced version, выпускавшаяся from 1954 to 1956.
Was issued 216 006 sedans and 17 742 convertible. The price of the car was 8000 RUB.
Background
The production of passenger cars in the Soviet Union began in the thirties, with models of the medium and big, the Gorky plant and Moscow named after Stalin. It was relatively large cars with powerful engines of a large working volume.
They are widely used in the national economy of the country, in the taxi (including ZIS), received on the distribution or acquired various state institutions, but in the broad retail sales have never been. A number of passenger cars, however, all the same was received by the citizens in the form of valuable gifts for different kinds of services (for example, in Moscow in the beginning of 1937 were subject to forced exchange of the «Emka» with an additional charge on credit including about 1 000 private GAS-AND to go to the peripheral areas) or, for example, as a win in the гослотерее - and, in any case, as one of the prizes was even the luxurious Executive ZIS-101, as well as purchased under special permits - in particular, «Эмка» cost 9 thousand rubles.
One way or another, to the end of the thirties, at the background of the ongoing by the time of mass motorization in the countries of the West, the country's leadership began to understand, that only public transport will not be able to fully provide for the needs of society. In addition, the car was considered as a good means of motivation and encouragement. Thus arose the interest to create relatively accessible and affordable in the production of «compact» car, which was designed primarily for sale to the public for personal use, which coincided with the accumulation by the time of the Russian industry necessary for mass production of this type of car-building (earlier drafts of «up», such какНАМИ-1 and NATI-2, could not be implemented as of times because of the absence in those years, the necessary production capacity and experience of the mass serial production of motor transport).Even in the prewar years, the Moscow plant of the international Communist youth (KIM) was using the number of foreign analogues developed a «compact» KIM-10. The main prototype was inexpensive, but is fairly modern and technological in mass production, the British model of Ford Prefect. Design, former quite modern for subcompact 1940, was formed from The designer's. Brodsky.
In 1940, began малосерийное production KIM-10-50 (two-door sedan) and KIM-10-51 (two-door convertible, at different terminology - Phaeton). Later was developed KIM-10-52 - version with a body «four-door sedan, a more practical in Soviet conditions, which serially was never released.
It was released a total of about 450 copies of all the options KIM-10. Opening in may in the sale of the party was sold out to the beginning of the war. In the years of the war the plant was rerouted to the production of more relevant in times of war production.
History of creation
During and after the Second world war in the USSR in mass quantities (about 50 thousand pieces) were captured cars, mainly of German production. Many of them were one way or another in the hands of individual owners. Began and reparations deliveries of new cars, assembled in the Soviet zone of occupation - first of all BMW models 321 and BMW 340, gathered at the enterprise «Автовело» (former factory BMW) in Eisenach (later it was renamed in EMW, in order to avoid conflicts with the firm BMW).
Thus, the emergence of massive amounts of private vehicles has become in the post-war years spontaneously fait accompli.
Nevertheless, the captured fleet in the conditions of bad roads, lack of spare parts and the qualified repair quickly wear.
Hence the urgent need for the establishment of mass production of its Soviet-vehicle, intended for sale in individual use and the most suitable for use in domestic road conditions.
It is quite logical, that the prototype of it was decided to search among the German models - in addition to the traditionally high technical level of the German aircraft, the impact and the fact that they were in those years are quite common in the USSR, and many of their models were well familiar to drivers and mechanics, and on some models, made in East Germany, there were production documentation and even accessories for the production.
Considered several options. For example, offered widespread in pre-war Germany and the post-war USSR model DKW F8, it's a simple design, low cost in production and a very ремонтопригодная, with a predominantly wooden and plywood body (in the USSR abbreviation of DHQ jokingly interpreted as a «tree-glue-water») in the light of the bearing frame and with two-engine.However, concerns have been raised about the low durability of wooden body in the conditions of the climate of the greater part of the territory of the USSR, and in addition - DHQ had front-wheel drive, which was assessed very negatively from the point of view of the vehicles, the only двухдверные body and technically imperfect, relatively guzzler two-stroke engine insufficient capacity.
Subsequently the production of DKW F8 and the modernized model F9 was started in East Germany, and later the modernization of the line of cars has led to the appearance of the light of the famous «Trabant» and a few less well-known «Wartburg».
Ultimately, the choice fell on the model of Opel cadet K38 - relatively fresh, which was in production since 1937, a well-established for mass mass serial production, well proved itself in the domestic road conditions, with a sufficiently strong bearing all-metal body and relatively powerful (1074 cm3, 23 HP.) four-stroke engine.
As a model of «Кадетт» produced in November, 1936 (factory designation of the model - 11234). In late 1937, it was modernized - externally this resulted in the emergence of a new semi-circular mask radiator instead of the earlier of the flat and other small differences, after which he labeled «К38». For those years, it was a perfect technically, durable and comfortable car. There were versions with different types of body: - two - and four-door sedans (according to the terminology of limousines), a two-door кабриолимузин.
At the same time with the basic К38 also produced its cheaper, a simplified version of the - KJ38 (J - «Junior»), who mainly dependent front suspension, separate from the body frame, the lack of rear bumper, and a simplified finish, and Opel Olympia - a more perfect model, with the same body (except for the hood, which was аллигаторного type, opening the forward - instead of used to the side of the «Кадетта»), but equipped with more modern верхнеклапанным (OHV) engine displacement 1488 cm3 and a power of 37 HP.
For release in the USSR was selected Opel cadet K38, and in one of the most expensive and therefore quite rare variant - четырехдверном and with independent front suspension; in some sources indicate, with reference to the Resolution of the GKO № 9905 from 26 August 1945 «On the organization of the production of the МЗМА vehicle Opel-Kadet To-38 in its present form», that the choice of this modification was carried out personally by Joseph Stalin, he was introduced ban on the introduction of any changes in the design.
Further information in the sources varies.
Some of them, such as Yuri Dolmatovsky in the book «I need a car, reported that the car was produced entirely or almost entirely on the equipment and documentation administration of the plant «Opel» in Рюссельхайме (by the way, who was in the American occupation zone) and assembled in the USSR.The historian of the automotive industry lion Шугуров reports in his book «the Cars of Russia and the USSR», the technical documentation on the car was gone, and it had to be started on ready-made samples, as well as individual surviving elements of the technological equipment - primarily for the manufacture of doors, the most complicated in the production of the element body.
In the memories of some of the workers of the plant, заставших the preparation of the first issue of «Moskvich» for example Alexander Fedorovich Andronova (chief designer AZLK over the years from 1949 to the mid 70-ies), it is stated that the Department of the chief designer was preparing drawings independently, and production tooling supplied GAS, ZIS and other Soviet enterprises.
In General, given the confusion of the last war and the first post-war years, it can well be assumed that the documentation and part of equipment for shot with production still in 1940 the car were so or otherwise lost or destroyed, the more the plant in Рюссельхайме in the years of the war, the details of the issue of aircraft engines and has repeatedly бомбился aviation Allies.
Either way, the modern sources based on substantial documentary evidence restore events of those years as follows.
After the end of the war the plant Opel in Рюссельсхайме was in the American zone of occupation. However, according to the Berlin conference in the summer of 1945 the Soviet Union as part of the reparations received the right to the fourth part of the whole remaining in the West of Germany industrial equipment, including - to and from the Opel factory in Рюссельхайме.
Meanwhile, the de-facto Opel plant at that time lay in ruins: cars there have not been produced since 1940, due to the loading of military products, like aircraft engines for the bombers, and in August 1944, he was subjected to a large-scale bombing of the Federal aviation. As a result of export there was practically nothing. We managed to find only a snap-in for the manufacture of some components of the chassis and двухдверного variant of the body.
Therefore, a significant part of the lost documentation and equipment for the production of been recreated, and the works were produced in Germany by order of the Soviet military administration (Smad) forces mixed labour collectives, composed of seconded Soviet and volunteers of the German specialists, who worked in the created after the war of design bureaus.
The body of the воссоздавало KB in the city Шварценберге, which employed 83 German specialist under the direction of the Soviet engineer On. In. Дыбова. In it and were in 1945-1946 years of the reconstructed drawings and documentation, have been established wooden «muster-model» (the master-model) and templates for manufacturing of stamps. Work on reconstruction of power unit was carried out in Berlin, also German experts in the amount of more than 180 (including six professors) under the guidance of Professor MAMI IN. And. Soroko-Novitsky. Options with wooden bodies of «van» and «universal» were developed in the KB on the basis of former plants of the company Auto Union in Chemnitz, Цшопау and Zwickau, before the war, producing wooden bodies for car DKW and had a great experience in their design and manufacture.Thus, according to this version of the car in essence was developed to a large extent -- though as a copy of the pre-war «Cadet». Subsequently involved in the reconstruction of the automobile cluster munitions were disbanded, and the information did not appear in print until very recently.
It should also be noted that in the West, the production of «Cadet» resumed after the war was not, but was it more perfect version - Opel Olympia OL38. Thus, one can assume that the documentation and equipment are still preserved, either were also partially reconstructed.
Also, even before the war in France on the basis of the models of the cadet and Olympia, although with a much lower volume of borrowing, was created his own version of the car-Renault Juvaquatre, выпускавшаяся with a break in the 1937-1960 years.
One way or another, already on December 4, 1946, a year and a half after the start of preparation of production, the Plant of Small Cars (ZMA, so after the war was renamed the former KIM) issued the first copy of the new model, which received the name of «Moskvich-400». Or, if fully follow the original system of nomenclature those years, " Moskvich-400-420 g»: the first was the number of the engine, the second - of the body.
In those years, this car, as a rule, simply called «Muscovite», as other «Muscovites» then was not.
Soon after the sedan appeared wooden wagons «Moskvich-400-422» (1949-1956), convertibles «Moskvich-400-420А» (1949-1952) and of the chassis with cab «Moskvich-400-420Б» (1954), in which were established a variety of cargo body, made bodywork plant Минпищепрома in Moscow.
It is curious, that the state acceptance tests of the car went through a «retroactive» - only in 1949, already in the course of its serial production.
In 1947, the 800 anniversary of Moscow ZMA issued the «jubilee» party of cars, which on the left боковинке hood memorial sign in the form of a ancient shield.
There was also the medical version of 420М, which was driving over the windscreen, washable upholstery of interior and a set of medical equipment inside.In may 1951, appeared upgraded gearbox with a more convenient shift lever on the steering column.
In 1954 had a more powerful engine model - 401 (26 h.p.). Accordingly, changed the designation of the car - now the base sedan called the «Moskvich-401-420».
The production of the «Muscovites» grew rapidly: 10-thousandth car descended from the conveyor in 1950, and soon it has already reached the annual output of 35 000 - 50 000 pieces. Cars go on sale at the price of 8 000 roubles («Moskvich-401» - 9 000; «Victory» GAZ M-20 has cost 16 000, «ZIM» GAZ-M-12 - 40 000 rubles; the average salary in the national economy of the USSR in 1950, was 601 of the ruble). The model was not very popular, but already in the early fifties, the demand for cars has grown substantially, and the «Muscovites» and «Victory» had already been formed a queue of those wishing to buy them («ZIM» was not in demand because of the extremely high prices, and although because of this, he was in free sale, real sold the car for personal use, there was very little).
Technical characteristics
«Moskvich-400/420» and «-401/420» (data for «Moskvich-401» given in parentheses)
Carrying the body, 4×2: 4-seater 4-door sedan 420, 4-door convertible 420А, 3-door wooden wagon 422, 2-door pickup truck 420Б, 2-door all-metal wagon 420Б, 2-door wagon with a separate body 420Б (as IZH-2715), sanitary 420М, the aerodrome starting the engine APA-7 (chassis 400-420Э), experimental 5 doors wooden wagon 421.
Engine:
Capacity: 23 (26) HP 3600 (4000) rpm, 4-cylinder, 4-stroke, 1074 cm3. Compression ratio: 5,8(6,2):1. Cylinder diameter/ piston stroke: 67,5/75 mm. The gap between the pusher and the core of the valve: - intake - of-0.15 - 0.17 mm, outlet - 0,20 - 0,22 mm.
Order of work of the cylinder: Ah 1-3-4-2
Carburetor K-24, with falling stream.
Electrical equipment:
Battery: 3-STE-65, 6B, battery capacity - 65 A/h.
Type and power of the generator: Г28, 100W.
Type and capacity of starter: ARTICLE 28; 0,6 HP.
Type of spark plug: AT-11/10A, JV. М14х1,25; the gap between the electrodes: 0.60 - 0.70 mm.
Length: 3 855 mm, width: 1 400 mm, height: 1 545 mm, base: 2 340 mm, height: 190 mm under both axes.
The track of the front wheels: 1 105 mm;
The convergence of wheels: 1.5-2.5 mm; the collapse of the wheels: 42'; the angle of inclination of rotary steering sideways: 7 degrees; forward: 0 degrees.Rear track: 1 170 mm.
Turning radius: 6.00 m.
Angles of entry: front 35 degrees, rear - 23 degrees.
Clutch: a single-disk dry. Free running of a pedal of coupling: 18-24 mm.
Transmission: 3-speed + 1 rear.
Number of gears : : I - of 3.56, II - 1.73 a, III - 1,00, reverse - 4.44 carats.
Final drive ratio: 5,14, a pair of bevel gears with screw teeth.
Front suspension: a type of «Дюбонне», the independent, шкворневая, 2 hydraulic shock absorber unilateral actions.
Rear suspension: on two longitudinal semi-elliptical springs, 2 hydraulic shock absorber unilateral actions.
Hydraulic drum brakes on all wheels.
Weight (without load): 845 (855) kg.
Maximum speed with full load by road: 90 km/h.
Tire size: 4,50x16 or 5,00x16 inches.
Tire pressure (bar): front - 2,00 or 1.75, rear - 2,30 or 2.00.
Fuel tank capacity: 31 l. Gasoline - A-66. Fuel consumption: at 9.0 l/100 km.
Cooling system capacity: 6,0 l.
The capacity of the oil Carter: motor - 2.7 l (with oil filter - 3.3 l); gearbox - 0,4 l; the differential - 0.9 l.
Basic modification
Moskvich-400-420 g (1946-1953) - four-door sedan;
Moskvich-400-420А (1949-1954 she) is a four-door кабриолимузин (body with an open top, but preserves the side and scope of the doors with glass);
Moskvich-400-420Б - model with manual control for persons with disabilities;
Moskvich-400-422 (1948-1956) - a truck with a wooden frame of the body;
Moskvich-400-420К - chassis for mounting of various bodies;
Moskvich-400-420М - for home health care, from different 400-420 g only markings;
Moskvich-401-420 (1954-1956) - advanced sedan;
Moskvich-401-420Б - modernized a modification of the sedan;
Moskvich-401-422 (1954-1956) - деревометаллический the van;
Just released: 216 006 sedans, 17 742 convertible, 11 129 vans, respectively 422 and 2 562 pickup trucks and vans 420Б.
It is curious, that on the basis of the first «Moskvich» one time produced кабриолимузины - according to the German model, there is such a body was used in the pre-war years the popularity and there were in the model the rows of many manufacturers, including Opel, and after the war are often issued in the form of conversion of serial cars forces small body Atelier. However, the original кабриолимузин Opel cadet had two doors, and the Soviet was designed anew for on the basis of the four-door sedan.However, in spite of the efforts to stimulate demand unprecedented for post-war years, the reduction of the retail value of the open of the body compared to the closed (in fact cabriolet on the basis of the private car, especially with the monocoque body, costs in the production of much more expensive, and therefore the cost of such car is always higher than that of similar to a closed body), the Soviet motorists in no hurry to acquire convertibles in view of their obvious impracticality in the climate of much of the country is a relatively high demand for them was only in the southern republics of the Union.
Many convertibles were subsequently converted into ordinary closed vehicle by welding of the roof. Surprisingly, but in recent years there has been strictly opposite trend - in the remaining conventional «Muscovites» enterprising traders cut down the roof in order to pass them off as the surviving кабриолимузины. In fact, in the present time of complete factory cabriolets «Moskvich» around the world, there are units.
Experienced options
Moskvich-400-421 (1948-1950) - wagon, made a few experienced copies.
Moskvich-Э403-424 (1949) - the pilot sedan, built a small test of the party. Different modified design, the hood аллигаторного type. The engine is mounted Moskvich-403 (not to be confused with the serial «Muscovite-403»the end of the 1950-s - early 1960-ies).
Pick - up soon after the release of 400-th family directly on МЗМА, perhaps, on the chassis of "Moskvich-400-420К" has produced several versions of pickup trucks (there were not less than three species, including one that is designed to work with a trailer). However, in a series he did not go. According to some information, this model was to get the index of "420Б", but, in view of the refusal of the plans of its serial production, the index of "B" was subsequently assigned a version with manual control.